Clinical Trials in the Baltic States – Countries’ Profile for 2023
In recent years the Baltic States, comprised of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, have become a formidable destination for conducting clinical trials due to its mature healthcare systems and rational regulatory reforms.
On the one hand, the Baltic states abide by the same international standards and agreements as other EU countries, and, on the other, the low cost of living and affordable clinical trial services make the Baltic States very attractive for clinical stage biopharmaceutical companies. There is also a high level of interest from patients to participate in clinical studies which positively impacts recruitment thus shortening timelines and further reducing the trial budgets. There are currently 605 clinical trials being conducted in the region.
The Baltic States have established themselves as a place to conduct high-quality and economical trials and are likely to remain an attractive choice for multicountry clinical research going forward.
Region Overview
Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania are small neighboring countries that are located in the northeastern region of Europe on the Baltic Sea coast.
Estonia
Estonia, the northernmost country out of the three Baltic States, borders the Baltic Sea and the Gulf of Finland and is renowned for its vast forests, lakes, and beaches. The largest city and capital is Tallinn, with a population of around 450,000. The official language is Estonian.
Latvia
Latvia is located between Estonia and Lithuania. The country’s capital and largest city is Riga, with a population of around 640,000. The official language is Latvian. Latvia is a diverse country with a rich cultural heritage.
Lithuania
The southernmost of the three Baltic States, Lithuania is the largest and most populous country in the region. The country’s capital and largest city is Vilnius. Lithuania is known for its production of amber, a gemstone that is found along its Baltic Sea coast. The official language is Lithuanian.
Despite their small size, the Baltic States have a rich history and culture. The three countries share many similarities but also have their own unique characteristics and traditions.
Demographics
Estonia
Estonia has a population of approximately 1.3 million people with 40% of the population between the ages of 25 and 54. Most people live in urban areas (69%). The main ethnic group is Estonians (68%). Their life expectancy is 79.1 years.
Latvia
Latvia has a population of approximately 1.8 million people with 41% of the population between the ages of 25 and 54. Most people live in urban areas (68%). The largest ethnic group is the Latvians, who make up about 62% of the population. Their life expectancy is 75.7 years.
Lithuania
Lithuania has a population of approximately 2.7 million people with 39% of the population between the ages of 25 and 54. Most people live in urban areas (68%). The largest ethnic group is the Lithuanians, who make up about 86% of the population. Their life expectancy is 76.4 years.
Healthcare Sector
All three Baltic states have universal healthcare systems, providing access to healthcare services for their citizens. The healthcare systems are predominantly funded through taxes and social security contributions. Over the years, the Baltic states have invested in modernizing their healthcare infrastructure. They have improved and expanded their hospital facilities, equipped them with advanced medical technologies, and established specialized medical centers.
The Baltic States are home to modern medical institutions and research centers, where healthcare professionals receive continuous training, conduct medical research, and contribute to advancements in healthcare knowledge and practices.
The Baltic states actively participate in international healthcare collaborations, including partnerships with other European countries and engagement in research networks. They strive to learn from best practices and share their experiences in healthcare delivery.
Reasons to Conduct Clinical Trials in the Baltic States
The advantages of selecting the Baltic states as the destination for conducting clinical research include:
- Excellent clinical sites’ infrastructure
- Skilled medical professionals
- A large pool of treatment-naïve patients
- Clinical practices are in line with the European standards of care
- Motivated and well-educated investigators
- Competitive costs of running clinical trials
- Prompt site contracting and study start-up
Snapshot of Clinical Trials in the Baltic States
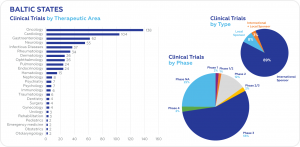
According to recent data from clinicaltrials.gov, the largest number of ongoing clinical trials are conducted in oncology (138), followed by cardiology (104), gastroenterology (62), and neurology (55). Most trials are in Phase 3 (56%). International sponsors conduct 89% of all ongoing clinical trials.
Baltic States: Quick Facts
Regulatory approval process
The application must be uploaded onto the Clinical Trials Information System (CTIS). Parts I and II of the documents are assessed in parallel within 45 calendar days (60 calendar days in total for review and approval).
Agreements with sites and investigators
Having a country-specific Clinical Trial Agreement template in place can greatly reduce the negotiation timelines.
EC review and approval
CEC is the only ethics body involved in the review process. Submission is done via the CTIS.
Favorite trial sites’ locations
Estonia – Tallinn and Tartu.
Latvia – Riga and regional centers such as Daugavpils, Liepaja, Valmiera, and Rezekne.
Lithuania – main medical centers are located in major cities such as Vilnius, Kaunas, and Klaipeda.
Legal entity
It is not mandatory to have a CRO representative as the applicant. There are, however, sections of the CTIS application form that should be filled out in the local languages. Submissions to the CEC also need to be completed in either local or in both English and local languages. The assistance of local staff is therefore recommended.
QP Declaration / GMP certificate
A declaration from the QP stating that the manufacturing site operates in compliance with the EU GMP is required for submission.
Documents requiring special attention
The Informed Consent Form (ICF) should be completed in the local language and contain country-specific information.
Official language
Essential documentation should be submitted in English. Patient-related documents, labels, protocol synopsis should be translated into local languages.
Patient insurance
A Global insurance agreement with the local legal entity in the country is required. A further requirement is that a local contact who speaks the local language should be available to assist the patient with any questions.
Useful tips
Initial submissions made before 31 January 2023 and submitted under the old legislation (Clinical Trial Directive 2001/20/EC) can continue, based on the assumption that the trial will be completed by January 30, 2025. Processes will remain unchanged, and sponsors will therefore be able to submit substantial amendments and end-of-trial notifications as required under the Clinical Trial Directive.
Regulatory Environment for Clinical Trials in the Baltic States
On 31 January 2022, the EU Clinical Trials Regulation No 536/2014 (CTR) became applicable in all EU/ European Economic Area (EEA) Member States, thereby replacing the EU Clinical Trials Directive (2001/20/EC) (CTD).
Effective January 31, 2023, all new CTAs must be submitted under the EU Clinical Trials Regulation via CTIS.
To perform clinical trials in Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, the CTR requires that all CTIS User Administrator/User submit a harmonized format of the application dossier consisting of Part I (Scientific Review documents) and Part II (Ethical Review documents).
The Clinical Trials Regulation No 536/2014, Annex I, requires that a comprehensive list of documents is submitted. The CTIS User Administrator/User can submit Part I and Part II either simultaneously or sequentially.
The General timeline from study submission until initial approval is 60 days (validation – 10 days; assessment – 45 days; decision – 5 days). Parts I and II can be assessed in parallel within 45 calendar days and up to 76 calendar days if there are any requests for information.
Cromos Pharma – your partner in International Clinical Research
Cromos Pharma has an experienced local team that effectively manages regulatory and contracting processes to ensure that studies can be initiated in the shortest period possible. We recruit highly educated and experienced staff that assures that each trial managed by our team in the Baltic States produces exceptional data quality and reliable results.
Cromos Pharma combines global expertise with in-depth local experience and knowledge that translates into exceptional patient recruitment. Our team has met or reduced enrollment timelines in 95% of the conducted trials.
If you are considering conducting clinical trials in the Baltic States or in any of the other countries where Cromos Pharma is active, our team will be happy to answer your questions.